ow let's focus on the Manual partitioning of ParrotOS using Calamares installer, which may be necessary for various purposes and needs.
Like the Dualboot with Windows, this method allows you to assign the desired size of the partitions and determine how many of them to create or edit.
Let's see two use cases:
Case 1: Partitioning a disk with existing partitions
After following the steps for setting the Parrot Installationbefore partitioning, select Manual Partitioning then click on Next.
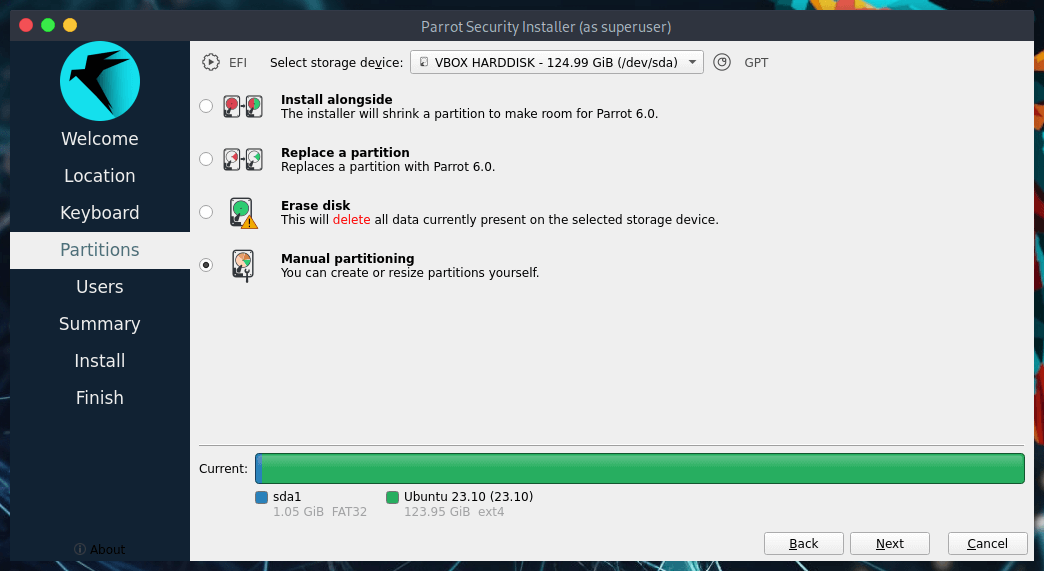
You'll see something similar to this:
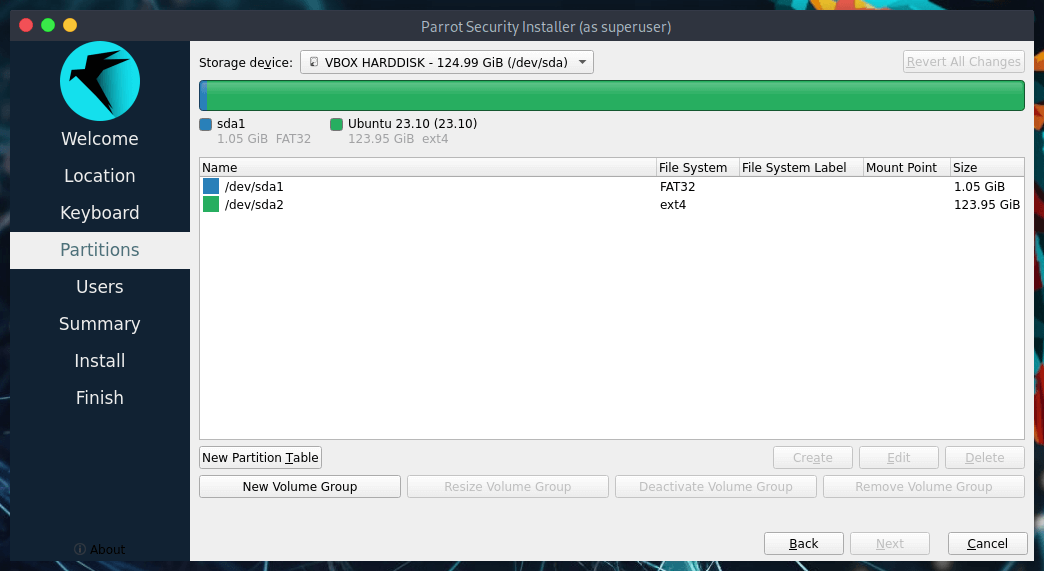
The partitions in detail:
/dev/sda1is the partition which contains EFI boot files./dev/sda2is the partition containing the existing OS.
To make ParrotOS work in a UEFI computer, at least three working partitions are needed:
/boot/EFI- the folder containing the efi firware necessary to boot the system./- the folder containing the entire system/home- the User data folder
Note
Disable Secure Boot and CSM from UEFI settings in your machine before doing any of the above descripted operations.
In a standard BIOS partition, at least two working partitions are needed:
//home
Now, let's change the mount point for the necessary partitions. First, select /dev/sda1 and click on Edit 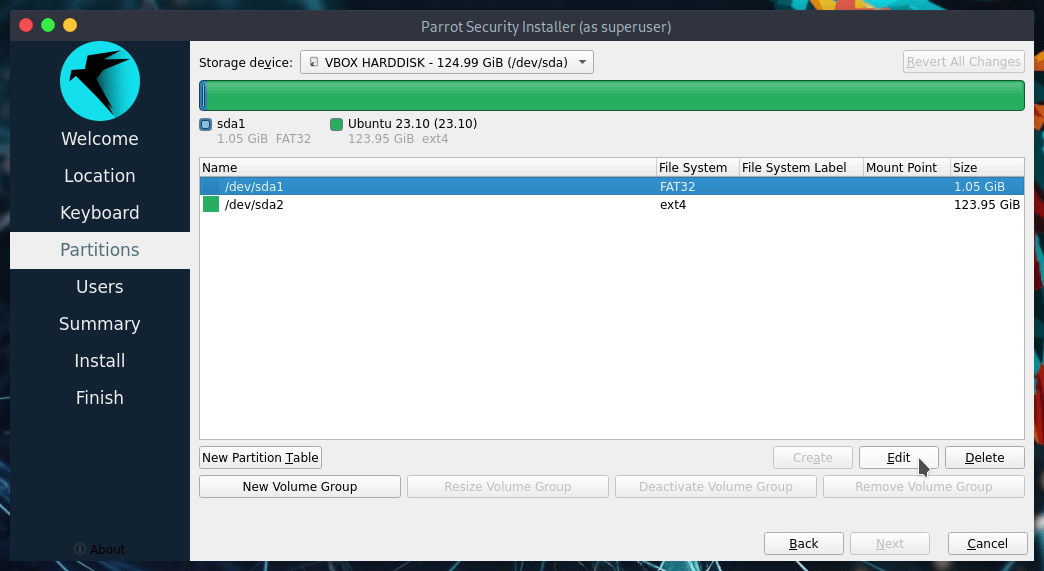
This window will appear, here is possible to shrink/resize partitions (by dragging the bar or inserting the size in MiB), set flags and mount point.
Set up the partition as you can see below, then click on Ok.



0 commenti:
Post a Comment