OpenELEC (short for "Open Embedded Linux Entertainment Center") is a free and open source embedded operating system providing a complete media center software suite that comes with a pre-configured version of XBMC and third-party addons with retro video game console emulators and PVR plugins. OpenELEC is an extremely small and very fast booting Linux based distribution, primarily designed to be booted from flash memory card such as CompactFlash or a solid-state drive, similar to that of the XBMC Live distribution but specifically targeted to a minimum set-top box hardware setup based on an Intel x86 processor and graphics.
The OpenELEC team released the second Release Candidate for OpenELEC 3.0 on 26 January 2013. The team has updated XBMC to latest XBMC Frodo and fixed some issues found in their first Release Candidate and further updated some important parts of the operating system to fix issues and add additional drivers.
On 5 February 2013, OpenELEC announced their new partnership with ARCTIC - a company based in Switzerland best known for their cooling solutions. Together, they developed a fully passive cooled Entertainment system - the MC001 media centre, equipped with their latest XBMC 12 (OpenELEC 3.0) platform. OpenELEC and ARCTIC are planning on their next release to provide a more dedicated builds for the ARCTIC MC001 systems.
GeeXboX is a free and open source Live USB/Live CD based Linux distribution providing a HTPC software suite for personal computers and ARM-devices that since version 2.0 comes with a pre-configured version of XBMC media center as its media player and GUI.
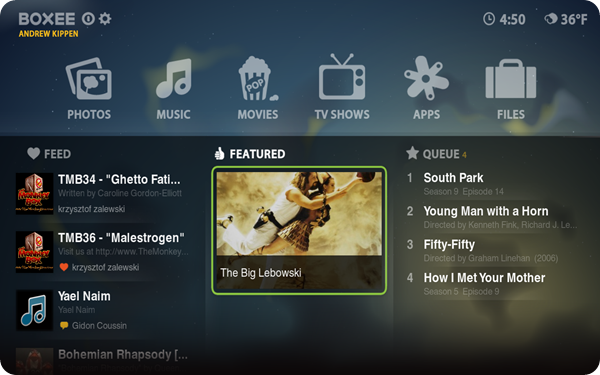
Boxee, (produced by startup company Boxee Inc.), is a freeware and partially open source software cross-platform media center and entertainment hub with social networking features that is a commercial fork of XBMC software.
Boxee now supports Windows, Linux, and OSX, with the first Alpha made available on 16 June 2008. Boxee as a company is also an official sponsor of the XBMC development project. The last version was 1.5. There will be no more versions of the desktop versions, with new emphasis on the Boxee Box.
Commodore OS, full name Commodore OS Vision, is a free to download GNU/Linux distribution developed by Commodore USA and intended for its Commodore-branded PCs. The distribution is based on Debian and Linux Mint, available only for x86-64 architectures, and uses the GNOME 2 desktop environment and comes with several preinstalled software including XBMC media center.
DVDFab Media Player by Fengtao Software Inc. is a media player software for Windows, based on the XBMC source code. DVDFab Media Player can play encrypted and DRM-protected Blu-ray Discs for 60-days for free before it has to be licensed to enable that feature again. It can however playback unencrypted and Blu-ray ISO-images, folders, and other DRM-free media files without a license.
iConsole (formerly known under the project codename "Full Circle"), produced by startup company MechaWorks, is a freeware and partially open source media center and entertainment hub with video game console features that is initially a fork of XBMC and Boxee software.
The first public Alpha release will be as a Linux based distribution, primarily designed to be installed on a computer's empty harddive to make a computer in to a dedicated HTPC, similar to that of the XBMC Live distribution but specifically targeted to a minimum set-top box hardware setup.
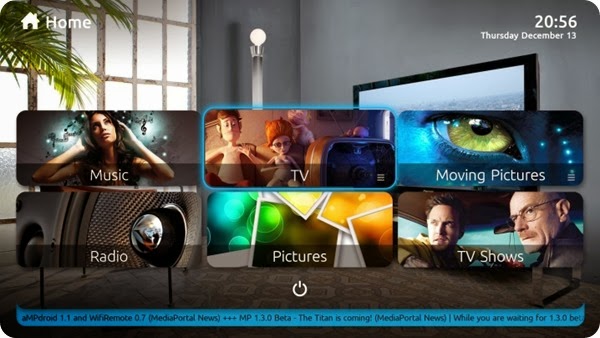
MediaPortal is free and open source software media center written for Microsoft Windows that is initially based on forked XBMC source code by Erwin Beckers (a.k.a. Frodo, who was also one of the original founders of XBMC) in February 2004. The reason for this fork to Microsoft Windows was to get away from hardware and software platform limitations of the Xbox game-console platform that XBMC development started on, mainly because of the Xbox inability to support TV-tuner adapters natively as Erwin wanted PVR functionality. Now after several years and innumerable feature changes there has been almost a complete re-design of the source code, however the skinning engine of MediaPortal 1.X.X still remains very similar to that of the original XBMC software making it relatively easy for people to port skins/themes back and forth between the two projects, something that is done quite frequently.
Pulse-Eight Limited sells both custom and off the shelf hardware solutions primarily designed for XBMC, such as remote controls, HTPC systems and accessories, including a custom HTPC PVR set-top-box pre-installed with XBMC that they call "PulseBox" Pulse-Eight also offers free performance tuned embedded versions of XBMC that they call "Pulse" which is based on OpenELEC and a custom PVR-build of XBMC that is meant to on your dedicated HTPC system.
Plex.
On 21 May 2008, XBMC developer Elan Feingold forked the source code of XBMC and started a new project called Plex, (previously this Mac OS X port of XBMC was informally known as the "OSXBMC" project). Feingold said that he would still try to collaborate with most Team-XBMC members behind the scenes and at least try to keep Plex skinning engine compatible with XBMC skins. While Plex began as a free software hobby project, since 2010 it is commercial software (freeware) that is today owned and developed by a single for-profit startup company, Plex, Inc., and today parts of what Plex offers is closed source proprietary software. The Linux, Macintosh, and Windows servers and clients are free, and offer their Android and iOS clients for a small one-time charge.
Feingold was the Team-XBMC member who first initiated the Mac OS X port of XBMC, but soon after he left the original XBMC project due to what was arguably a falling-out with rest of Team-XBMC's developer members over the team's majorities feeling that the XBMC project should aim for strict adherence to the GPL and always keep to an open-source software mindset. This disagreement is claimed to be one of the main factors that led Elan to leave the XBMC project and create the Plex fork.
Raspbmc is a light Linux distribution created by Sam Nazarko. It is designed as a media center for the Raspberry Pi and is based on Raspbian and XBMC.[58] Raspbmc was announced on 2 February 2012,[59] and achieved final release (version 1.0) on 3 February 2013.
Vu+ (or VUplus), is produced by a Korean multimedia vendor, which is a manufacturer of Linux-powered DVB satellite, terrestrial digital television receivers (set-top box) that all currently uses Enigma2 for Dreambox based software as firmware.
In September 2011 Vu+ Day in Amsterdam it was announced that the next-generation Vu+ DVB satellite receivers to be released publicly in the end of 2012 will be using XBMC Media Center software for its GUI, a development project that they call "XBMC4STB" (XBMC for Set-Top-Boxes), with beta releases of both the software and hardware said to be made available to XBMC developers before then .
Voddler is a commercial video-on-demand service and client software streaming movies and television programming, similar to Spotify and Grooveshark but for video. From its first release at 1 July 2009 up until 24 February 2010, Voddler's media player software was initially based on a fork of the XBMC open source code.Voddler violated the license for XBMC's source code by neglecting to release all of their modifications that they used in their application as required per the GPL, and they have been publicly criticized for this
Voddler's newer media player software is since 8 March 2010 now instead based on the Adobe Air closed-source application platform.
ONEvision by at-visions Informationstechnologie GmbH, (an international system integration and IT soutsourcing firm for hotels), ONEvision is a commercial fork of XBMC for use as hotel television system software in hotel environments and in the hospitality industry for in-room entertainment. It offers a platform for in-room service bookings and an IPTV interface, with custom theme branding. ONEvision is currently used throughout Europe and Asia at hotels such as Hyatt EMEA, Ramada Vienna, RIMC International, DWA Bratanki, Rogner International, EH&A, Heritage Hotel Hallstatt, St. Martins Therme, and Heiltherme Bad Waltersdorf. As of October 2010, at-visions as a company is also an official sponsor of the XBMC development project.
Element OS is a free embedded operating system designed for use on a Home Theater PC (HTPC) which is connected to a HDTV. Element OS is a Linux based distribution similar to that of the XBMC Live distro, however it comes preloaded with dozens of applications for listening to, viewing, and managing music, videos, photos, and internet media. XBMC is the pre-installed default media center, but Boxee and Hulu Desktop are also installable.
Sabayon Linux is a full Linux distribution that among other applications comes with a preinstalled and preconfigured "ready-to-use" version of XBMC Media Center.
Qt Media Hub (also known as QtMediaHub or Qt MediaHub), by Nokia, is a proof of concept port of XBMC to QML and Qt framework on ARM platforms for the MeeGo, Maemo, and Mer projects, to demonstrate the power and flexibility of using Qt/QML, and also to show the best practices when using Qt/QML.
yaVDR (which name originated from the abbreviation "yet another VDR") is an Ubuntu-based Linux (i386) distribution designed for Home Theater PC (HTPC) with TV tuner card for DVR (Digital Video Recorder) capabilities. yaVDR comes preinstalled and preconfigured "ready-to-use" version of XBMC Media Center from the "PVR" Subversion development branch as its primary front-end media player interface, with VDR (Video Disk Recorder) integrated as its PVR back-end server. It also features xine as an alternative front-end media player interface to XBMC.
XBMC for BSD, which is a full port of XBMC to BSD UNIX operating-systems. Compatible with FreeBSD and other similar derivatives like PC-BSD, for IA-32/x86, x86-64, PowerPC (G4 or later), and ARM-based computers, including hardware accelerated video decoding via VDPAU API on Nvidia's GPUs and VAAPI API for AMD/ATI Radeon.[92][93][94][95][96]
XBMC4XBox
XBMC4Xbox is a third-party developer spin-off project of XBMC, with still active development and support of the Xbox platform. This project was created as a fork of XBMC as a separate project to continue having a version of XBMC for the Xbox hardware platform. It was not started by official members of the official XBMC project, nor will it be suppoted by the Official Team XBMC in any way. It started when support for the Xbox branch was officially dropped by Team XBMC, which was announced on 27 May 2010.
If you liked this article, subscribe to the feed by clicking the image below to keep informed about new contents of the blog:























0 commenti:
Post a Comment